
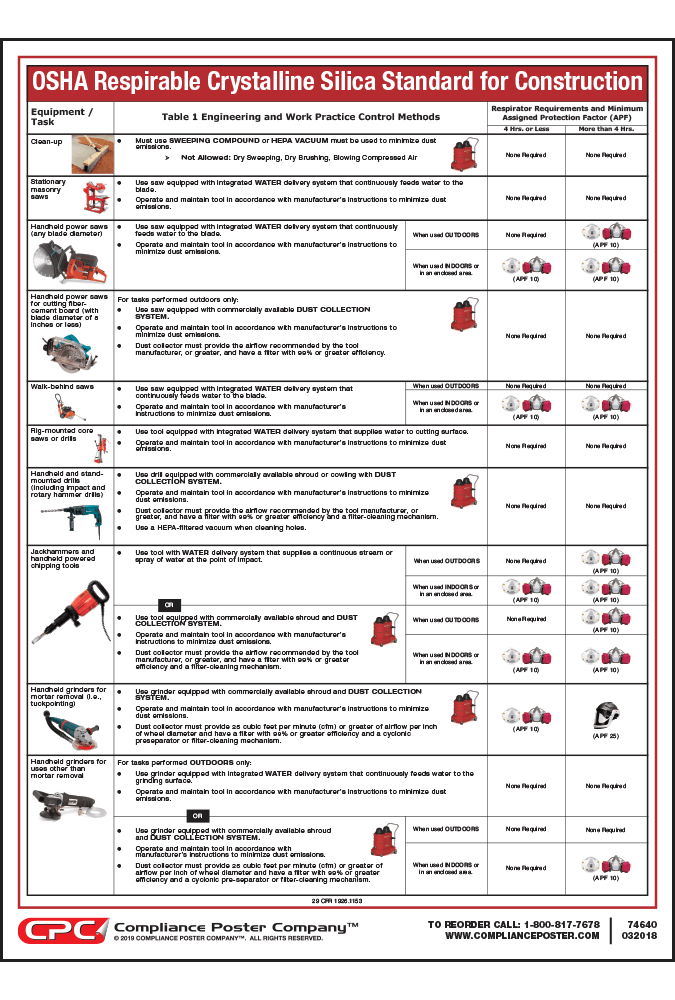
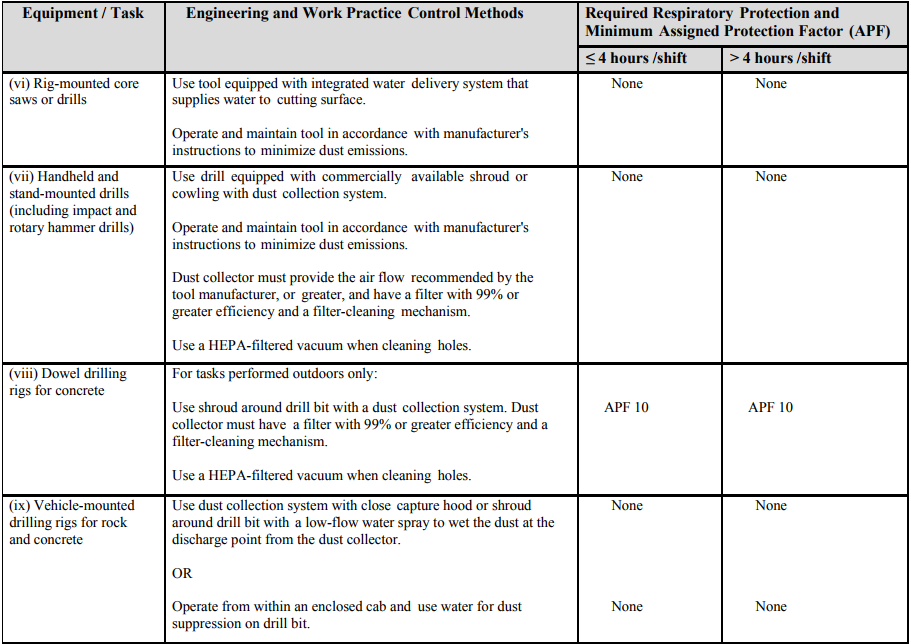
OSHA has identified carpenters, plumbers, and electricians as types of workers who may perform tasks ( e.g., drilling with a handheld drill) involving occasional, brief exposures to silica that are incidental to their primary work. Some examples of tasks that could generate very high short-term exposures include abrasive blasting and grinding, which are typically associated with high levels of visible dust. Short-term silica exposures must be very high in order for those exposures to reach or exceed 25 μg/m 3 as an 8-hour TWA for example, if an employee is exposed for only 15 minutes, his or her exposure would have to be higher than 800 μg/m 3 for that 15-minute period before the 8-hour TWA exposure would be at or above 25 μg/m 3. However, in many cases, employees who perform construction tasks for very short periods of time, in isolation from activities that generate significant exposures to silica ( e.g., some tasks listed on Table 1, abrasive blasting), will be exposed below the AL of 25 μg/m 3 as an 8-hour TWA under any foreseeable conditions. The standard does not include a specific exemption for tasks with only short-term exposures ( e.g., tasks with exposures for 15 minutes a day or less). The exception is intended to ensure that the standard does not apply to employees whose work results in only minimal silica exposures. The exception applies only where exposures below 25 μg/m 3 as an 8-hour TWA are expected or achieved without using engineering or other controls. OSHA's silica standard for construction applies to all occupational exposures to respirable crystalline silica in construction work, except where employee exposures will remain below the AL of 25 μg/m 3, calculated as an 8-hour TWA, under any foreseeable conditions. TWA - time-weighted average Scope (29 C.F.R.
#Osha silica standard professional#
PLHCP - physician or other licensed health care professional PEL - permissible exposure limit (50 μg/m 3 as an 8-hour time-weighted average) HEPA filter - high-efficiency particulate air filter The following acronyms are used throughout this document:ĪL - action level (25 μg/m 3 as an 8-hour time-weighted average) A short introductory paragraph is included for each group of questions and answers to provide background information about the underlying regulatory requirements. These FAQs provide guidance to employers and employees regarding the standard's requirements. OSHA developed these Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the standard in consultation with industry and union stakeholders. On March 25, 2016, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) published a final rule regulating occupational exposure to respirable crystalline silica (silica) in the construction industry (the standard). Frequently Asked Questions ("FAQs") for the Construction Industry

#Osha silica standard free#
In addition, the Act’s General Duty Clause, Section 5(a)(1), requires employers to provide their employees with a workplace free from recognized hazards likely to cause death or serious physical harm.
Pursuant to the OSH Act, employers must comply with safety and health standards and regulations issued and enforced either by OSHA or by an OSHA-approved State Plan. It is not a standard or regulation, and it neither creates new legal obligations nor alters existing obligations created by OSHA standards or the Occupational Safety and Health Act. This document is advisory in nature and informational in content.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
